Administrative divisions of the Republic of China
|
This article is part of
Administrative divisionsa series on the of the Republic of China |
||||||||||
| In effect | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Provinces (省 shěng) (streamlined) |
|||||||||
| Municipalities (直轄市 zhíxiáshì) |
||||||||||
| 2nd | Counties (縣 xiàn) |
|||||||||
| Provincial cities (市 shì) |
||||||||||
| 3rd | Districts (區 qū) |
|||||||||
| County-controlled cities (縣轄市 xiànxiáshì) |
||||||||||
| Urban townships (鎮 zhèn) |
||||||||||
| Rural townships (鄉 xiāng) |
||||||||||
| 4th | Urban villages (里 lǐ) |
|||||||||
| Rural villages (村 cūn) |
||||||||||
| 5th | Neighborhoods (鄰 lín) |
|||||||||
|
Suspended
|
||||||||||
| Compare Administrative levels and divisions of the People's Republic of China |
||||||||||
The Republic of China (ROC) currently administers two nominal provinces[1] and directly administers two direct-controlled municipalities:
- Provinces (streamlined)
- Taiwan Province; consists of the island of Taiwan, except the two municipalities, plus Penghu county (Pescadores Islands) and a number of outlying islands
- Sixteen counties
- Five provincial cities
- Fujian Province; consists of several islands offshore of the Chinese mainland:
- Kinmen County (Quemoy)
- part of Lienchiang County, namely Matsu
- Direct-controlled Municipalities
- Taipei City
- Kaohsiung City (also administering Dongsha Islands and Taiping Island of the South China Sea Islands)
These top-level divisions prescribed by the 1947 Constitution, which was drafted while the Kuomintang still controlled mainland China and kept in place to validate the ROC government's claim as the government of China. The provincial governments of Fujian and Taiwan have been largely streamlined, since 1949 and 1998, respectively.
Contents |
Special considerations
Streamlined provinces
Since 1949, the most controversial part of the political division system of the ROC has been the existence of the Taiwan Province, as its existence was part of a larger controversy over the political status of Taiwan. Since 1997, most of the Taiwan provincial government's duties and powers have been transferred to the national government of the Republic of China in the constitutional changes. The much smaller Fujian province consisting of Kinmen and Matsu, on the other hand, had most of its authority passed off to its two counties.
Joint Service Centers
The central government operates three regional Joint Service Centers (區域聯合服務中心) outside Taipei as outposts of the government ministries in the Executive Yuan, similar to the cross-departmental mode of working in the Government Offices in England. These regions, laid out the Comprehensive National Spatial Development Plan for Taiwan (臺灣地區國土綜合開發計劃), can be considered a de facto level of government, perhaps equivalent to de jure provinces or similar to the English regions. There is one regional service center for each of the Southern Taiwan Region (with the center in Kaohsiung), the Central Taiwan Region (Taichung), and the Eastern Taiwan Region (Hualien). The Northern Taiwan Region is served by Taipei, the central government's administrative headquarters and de facto capital.
Re-organization
There has been some criticism of the current administrative scheme as being inefficient and inconducive to regional planning. In particular, most of the administrative cities are much smaller than the actual metropolitan areas, and there are no formal means for coordinating policy between an administrative city and its surrounding areas.
Before 2008, the likelihood of consolidation was low. Many of the cities had a political geography which were very different from their surrounding counties, making the prospect of consolidation highly politically charged. For example, while the Kuomintang argued that combining Taipei City, Taipei County, and Keelung City into a metropolitan Taipei region would allow for better regional planning, the Democratic Progressive Party argued that this is merely an excuse to eliminate the government of Taipei County, which it had at times controlled, by swamping it with votes from Taipei City and Keelung City, which tended to vote Kuomintang.
On 1 October 2007, per legislation newly coming into force, Taipei County was upgraded to become a quasi-municipality (準直轄市) on the same level as Kaohsiung City and Taipei City.[2] It is allowed the organizational and budgetary framework of a de jure municipality, but is still formally styled as a county. The Taichung County and City are lobbying the central government for a similar status.
President Ma Ying-jeou of Kuomintang in his 2008 election campaign platform advocated for a rearrangement of three municipalities and 15 counties. Since his inauguration, his administration has started to prepare for this.[3] The city and county of Taichung is to merge in 2010 and join Taipei and Kaohsiung as a directly-controlled municipality. The city–county pairs for Hsinchu, Chiayi, and Tainan are aiming to merge in 2011, with the city annexed into an expanded county in each case. In 2011, Kaohsiung county will also be annexed by the Kaohsiung Municipality. Taipei County will move from quasi-municipality to de jure status in 2009, and in 2014 merge with the cities of Taipei and Keelung to form a larger municipality. The whole project is scheduled to complete in 2014, two years after the end of Ma’s first presidential mandate.
Proposals for the following were approved by the Ministry of the Interior on 23 June 2009: promotion of Taipei County to become Xinbei City (新北市) awaiting further merger with Taipei Municipality and Keelung City, the merger of Kaohsiung Municipality and County, and the merger of the City and County to form a promoted Taichung Municipality.[4] In the same meeting, the merger of the City and County of Tainan was referred to the Cabinet (Executive Yuan). This merger and promotion proposal was finally approved on 29 June 2009 to give the Tainan-fu Municipality (臺南府市), evoking the Qing-era name of the prefecture.[5] Follow-up legislation to give substance to this approval is expected in due course. The original Ma plan for three municipalities turned out four in the event.
Approved ROC municipalities in 2010
The ROC municipalities approved in 2010 were as follows[6]:
| Map | No. | Division name | Trad. | Simp. | Hanyu Pinyin | Abbr. | Population | Area (km²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png)
1
2
3
4
5
|
1 | Taipei City | 臺北市 | 台北市 | Táiběi Shì | 北 běi | 2,622,933 | 271.7997 |
| 2 | Xinbei City | 新北市 | 新北市 | Xīnběi Shì | 新 xīn | 3,849,492 | 2,052.5667 | |
| 3 | Taichung City | 臺中市 | 台中市 | Táizhōng Shì | 中 zhōng | 2,629,323 | 2,214.8968 | |
| 4 | Tainan City | 臺南市 | 台南市 | Táinán Shì | 南 nán | 1,873,681 | 2,191.6531 | |
| 5 | Kaohsiung City | 高雄市 | 高雄市 | Gāoxióng Shì | 高 gāo | 2,769,072 | 2,946.2527 |
Proposals for ROC municipalities and counties
| Proposals | Changes | June 2009 Population - Combine |
Current Area (km²) - Combine |
Map (before) | Map (after) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-A | Hsinchu City + Hsinchu County = Hsinchu County (新竹市 + 新竹縣 = 新竹縣) |
915,012 | 1,531.6864 | 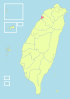 |
 |
.svg.png) |
|||||
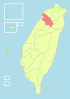
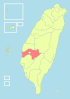
| 2-B | Chiayi City + Chiayi County = Chiayi County (嘉義市 + 嘉義縣 = 嘉義縣) |
821,721 | 1,961.6956 | 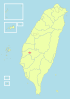 |
 |
.svg.png) |
|||||
| 2-C | Taipei City + Xinbei City + Keelung City = Taipei City (臺北市 + 新北市 + 基隆市 = 臺北市) |
6,854,715 | 2,457.1244 | 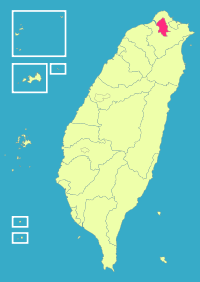 |
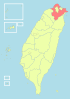 |
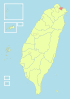 |
.svg.png) |
||||
Mainland China and Mongolia
Additionally, the ROC has not officially renounced its claims over mainland China and Mongolia. This results in a division of the mainland into 35 provinces, different from that of the current PRC system.
Structural hierarchy
The number at the end are the amount of entities as of June 2010, in areas under the ROC control:
| Level | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Division type |
Direct-controlled municipality (直轄市 zhíxiáshì) (2) |
District (區 qū) (49) |
Village (里 lǐ) |
Neighborhood (鄰 lín) |
|
| Province (省 shěng) (2) |
Provincial municipality (市 shì) (5) |
||||
| County (縣 xiàn) (18) |
County-controlled city (縣轄市 xiànxiáshì) (33) |
||||
| Urban Township (鎮 zhèn) (60) |
|||||
| Rural Township (鄉 xiāng) (226) |
Village (村 cūn) |
||||
| Total | 25 | 368 | 7,830 | 147,940 | |
Note:
|
|||||
The number of neighborhood, the lowest administrative level, is 147,940 under 7,830 villages in the ROC. And, to tell distinct neighborhood is from ordinal number, not from distinctive name. In total, there are 368 thirdly entities (rural and urban townships, county-controlled cities, and districts, in Chinese: 鄉鎮市區 xiāngzhènshìqū ).
In the ROC administrative scheme, a number of cities and counties have the same name, however, which are independent administrations. Tainan City and Tainan County, for example, which are completely different administrations. Generally, the biggest administrative area of structural hierarchy is direct-controlled municipality, then provincial city, and the last county-controlled city. In mainland China, the situation as is in reverse.
Direct-controlled Municipalities
| Romanization | Chinese | Tongyong Pinyin | Hanyu Pinyin | Wade-Giles | Pe̍h-ōe-jī | Pha̍k-fa-sṳ | City Seat | City Seat in Chinese |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 臺北市, 台北市 | Taibei | Táiběi | T'ai2-pei3 | Tâi-pak | Thòi-pet | Xinyi District | 信義區 | |
| 高雄市 | Gaosyong | Gāoxióng | Kao1-hsiung2 | Ko-hiông | Kô-hiùng | Lingya District | 苓雅區 |
Provincial Municipalities
In Taiwan Province:
| Romanization | Chinese | Tongyong Pinyin | Hanyu Pinyin | Wade-Giles | Pe̍h-ōe-jī | Pha̍k-fa-sṳ | City Seat | City Seat in Chinese |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 嘉義市 | Jiayi | Jiāyì | Chia1-i4 | Ka-gī | Kâ-ngi | East District | 東區 | |
| 新竹市 | Sinjhu | Xīnzhú | Hsin1-chu2 | Sin-tek | Sîn-tsuk | North District | 北區 | |
| 基隆市 | Jilong | Jīlóng | Chi1-lung2 | Ke-lâng | Kî-lùng | Jhongjheng District | 中正區 | |
| 臺中市, 台中市 | Taijhong | Táizhōng | T'ai2-chung1 | Tâi-tiong | Thòi-chûng | West District | 西區 | |
| 臺南市, 台南市 | Tainan | Táinán | T'ai2-nan2 | Tâi-lâm | Thòi-nàm | Anping District | 安平區 |
Counties
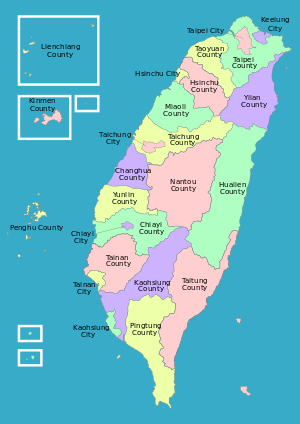
In ROC's administrative divisions , counties or Sien or Hsien (Traditional Chinese: 縣, Pinyin: Xiàn) are officially found in the second level; however, the streamlining of Taiwan Province has effectively made the county the first level below the Republic of China central government's rule. Within Fujian Province the county is still the second level. There are 18 counties administered by the Republic of China, including 16 in Taiwan Province and 2 in Fujian Province.
In Taiwan Province:
| Romanization | Chinese | Tongyong Pinyin | Hanyu Pinyin | Wade-Giles | Pe̍h-ōe-jī | Pha̍k-fa-sṳ | Capital | Capital in Chinese |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changhua County | 彰化縣 | Jhanghua | Zhānghuà | Chang1-hua4 | Chiong-hoà | Chông-fa | Changhua City | 彰化市 |
| Chiayi County | 嘉義縣 | Jiayi | Jiāyì | Chia1-i4 | Ka-gī | Kâ-ngi | Taibao City | 太保市 |
| Hsinchu County | 新竹縣 | Sinjhu | Xīnzhú | Hsin1-chu2 | Sin-tek | Sîn-tsuk | Zhubei City | 竹北市 |
| Hualien County | 花蓮縣 | Hualian | Huālián | Hua1-lien2 | Hoa-liân | Fâ-lièn | Hualien City | 花蓮市 |
| Kaohsiung County | 高雄縣 | Gaosyong | Gāoxióng | Kao1-hsiung2 | Ko-hiông | Kô-hiùng | Fengshan City | 鳳山市 |
| Miaoli County | 苗栗縣 | Miaoli | Miáolì | Miao2-li4 | Biâu-le̍k | Mèu-li̍t | Miaoli City | 苗栗市 |
| Nantou County | 南投縣 | Nantou | Nántóu | Nan2-t'ou2 | Lâm-tâu | Nàm-thèu | Nantou City | 南投市 |
| Penghu County (Pescadores) | 澎湖縣 | Penghu | Pénghú | P'eng2-hu2 | Phêⁿ-ô͘ | Phàng-fù | Magong City | 馬公市 |
| Pingtung County | 屏東縣 | Pingdong | Píngdōng | P'ing2-tung1 | Pîn-tong | Phìn-tûng | Pingtung City | 屏東市 |
| Taichung County | 臺中縣, 台中縣 | Taijhong | Táizhōng | T'ai2-chung1 | Tâi-tiong | Thòi-chûng | Fengyuan City | 豐原市 |
| Tainan County | 臺南縣, 台南縣 | Tainan | Táinán | T'ai2-nan2 | Tâi-lâm | Thòi-nàm | Xinying City | 新營市 |
| Taipei County | 臺北縣, 台北縣 | Taibei | Táiběi | T'ai2-pei3 | Tâi-pak | Thòi-pet | Banqiao City | 板橋市 |
| Taitung County | 臺東縣, 台東縣 | Taidong | Táidōng | T'ai2-tung1 | Tâi-tang | Thòi-tûng | Taitung City | 臺東市 |
| Taoyuan County | 桃園縣 | Taoyuan | Táoyuán | T'ao2-yuan2 | Thô-hn̂g | Thò-yèn | Taoyuan City | 桃園市 |
| Yilan County | 宜蘭縣 | Yilan | Yílán | I2-lan2 | Gî-lân | Ngì-làn | Yilan City | 宜蘭市 |
| Yunlin County | 雲林縣 | Yunlin | Yúnlín | Yun2-lin2 | Hûn-lîm | Yùn-lìm | Douliu City | 斗六市 |
In Fujian Province (Wade-Giles: Fuchien, Postal Romanization: Fukien):
| Romanization | Chinese | Tongyong Pinyin | Hanyu Pinyin | Wade-Giles | Pe̍h-ōe-jī | Pha̍k-fa-sṳ | Capital | Capital in Chinese |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lienchiang County (Matsu) | 連江縣 | Lianjiang | Liánjiāng | Lien2-chiang1 | Liân-kang | Lièn-kông | Nangan Township | 南竿鄉 |
| Kinmen County | 金門縣 | Jinmen | Jīnmén | Chin1-men2 | Kim-mn̂g | Kîm-mùn | Jincheng Township | 金城鎮 |
Re-organization plan in 2010
This plan will come into force in December 25, 2010.
| Level | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Division type |
Direct-controlled municipality (直轄市 zhíxiáshì) (5) |
District (區 qū) (157) |
Village (里 lǐ) |
Neighborhood (鄰 lín) |
|
| Province (省 shěng) (2) |
Provincial municipality (市 shì) (3) |
||||
| County (縣 xiàn) (14) |
County-controlled city (縣轄市 xiànxiáshì) (17) |
||||
| Urban Township (鎮 zhèn) (41) |
|||||
| Rural Township (鄉 xiāng) (153) |
Village (村 cūn) |
||||
| Total | 22 | 368 | |||
| Map | No. | Romanization | Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Pe̍h-ōe-jī | Pha̍k-fa-sṳ | City/County Seat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
Direct-controlled Municipalities (直轄市) | |||||||
| 1 | Kaohsiung City | 高雄市 | Gāoxióng | Ko-hiông | Kô-hiùng | |||
| 2 | Taichung City | 臺中市,台中市 | Táizhōng | Tâi-tiong | Thòi-chûng | Xitun District | 西屯區 | |
| 3 | Tainan City | 臺南市,台南市 | Táinán | Tâi-lâm | Thòi-nàm | |||
| 4 | Taipei City | 臺北市,台北市 | Táiběi | Tâi-pak | Thòi-pet | Xinyi District | 信義區 | |
| 5 | Xinbei City | 新北市 | Xīnběi | Sin-pak | Sîn-pet | Banqiao District | 板橋區 | |
| Taiwan Province (臺灣省,台灣省) | ||||||||
| 6 | Chiayi City | 嘉義市 | Jiāyì | Ka-gī | Kâ-ngi | East District | 東區 | |
| 7 | Hsinchu City | 新竹市 | Xīnzhú | Sin-tek | Sîn-tsuk | North District | 北區 | |
| 8 | Keelung City | 基隆市 | Jīlóng | Ke-lâng | Kî-lùng | Zhongzheng District | 中正區 | |
| 9 | Changhua County | 彰化縣 | Zhānghuà | Chiong-hoà | Chông-fa | Changhua City | 彰化市 | |
| 10 | Chiayi County | 嘉義縣 | Jiāyì | Ka-gī | Kâ-ngi | Taibao City | 太保市 | |
| 11 | Hsinchu County | 新竹縣 | Xīnzhú | Sin-tek | Sîn-tsuk | Zhubei City | 竹北市 | |
| 12 | Hualien County | 花蓮縣 | Huālián | Hoa-liân | Fâ-lièn | Hualien City | 花蓮市 | |
| 13 | Miaoli County | 苗栗縣 | Miáolì | Biâu-le̍k | Mèu-li̍t | Miaoli City | 苗栗市 | |
| 14 | Nantou County | 南投縣 | Nántóu | Lâm-tâu | Nàm-thèu | Nantou City | 南投市 | |
| 15 | Penghu County | 澎湖縣 | Pénghú | Phêⁿ-ô͘ | Phàng-fù | Magong City | 馬公市 | |
| 16 | Pingtung County | 屏東縣 | Píngdōng | Pîn-tong | Phìn-tûng | Pingtung City | 屏東市 | |
| 17 | Taitung County | 臺東縣,台東縣 | Táidōng | Tâi-tang | Thòi-tûng | Taitung City | 臺東市 | |
| 18 | Taoyuan County | 桃園縣 | Táoyuán | Thô-hn̂g | Thò-yèn | Taoyuan City | 桃園市 | |
| 19 | Yilan County | 宜蘭縣 | Yílán | Gî-lân | Ngì-làn | Yilan City | 宜蘭市 | |
| 20 | Yunlin County | 雲林縣 | Yúnlín | Hûn-lîm | Yùn-lìm | Douliu City | 斗六市 | |
| = Direct-controlled Municipality (直轄市) = Provincial City (省轄市 or 市) = County (縣) |
Fukien Province (福建省) | |||||||
| 21 | Kinmen County | 金門縣 | Jīnmén | Kim-mn̂g | Kîm-mùn | Nangan Township | 南竿鄉 | |
| 22 | Lienchiang County | 連江縣 | Liánjiāng | Liân-kang | Lièn-kông | Jincheng Township | 金城鎮 | |
Romanization
The romanization used for ROC placenames is Wade-Giles, however consistently ignoring the punctuations (apostrophes and hyphens), except "Keelung" and "Quemoy", which are the more popular versions of romanization. "Chiayi" and "Yilan" are bastardized forms of the Wade-Giles version, "Chia-i" and "I-lan", respectively. After Tongyong Pinyin was adopted by the Chen Shuibian administration in 2002, most municipalities, provinces, and county-level entities retained Wade-Giles, with the aforementioned exceptions. Taipei is, together with Taichung the only municipalities that use Hanyu Pinyin as standard and most street signs in Taipei have been replaced with Hanyu Pinyin, except for the place name "Taipei," which has retained the Wade-Giles spelling. With the Kuomintang (KMT)'s legislative and presidential electoral victories in 2008, Tongyong Pinyin will be replaced by Hanyu Pinyin as the ROC government standard, and will be the only official romanization system, starting in 2009.[7][8]
Claims over mainland China and Mongolia



After its loss of mainland China to the Communist Party of China in the Chinese Civil War and its retreat to Taiwan in 1949, the Kuomintang (KMT) continued to regard the Republic of China as the sole legitimate government of China and hoped to recover the mainland one day. Although in 1991 President Lee Teng-hui stated that the ROC does not challenge the right of the Communist Party of China to rule in the mainland, the ROC has never formally (by means of the National Assembly) renounced sovereignty over mainland China (including Xinjiang and Tibet) and Greater Mongolia. Most observers feel that the ruling Democratic Progressive Party would much prefer to officially renounce such sovereignty. This ambiguous situation results in large part because a formal renouncement of sovereignty over mainland China could be taken as a declaration of Taiwan independence, which would be unpopular among some circles on Taiwan and could likely bring about military action by the People's Republic of China.
Accordingly, the official first-order divisions of Republic of China remain the historical divisions of China immediately prior to the loss of mainland China by the KMT with Taipei and Kaohsiung elevated as central municipalities. These are: 35 provinces, 2 areas, 1 special administrative region, 14 centrally-administered (provincial-level) municipalities, 14 leagues, and 4 special banners. For second-order divisions, under provinces and special administrative regions, there are counties, province-controlled cities (56), bureaus (34) and management bureaus (7). Under provincial-level municipalities there are districts, and under leagues there are banners (127).
Maps of China and the world published in Taiwan sometimes show provincial and national boundaries as they were in 1949, not matching the current administrative structure as decided by the Communist Party of China post-1949 and including outer Mongolia, northern Burma, and Tannu Uriankhai (part of which is present-day Tuva in Russia)) as part of China (territories over which the PRC has renounced sovereignty). Recent moves by the DPP administration have been changing maps in school textbooks and official maps issued by the government to reflect the current divisions instituted by the PRC.
The current jurisdiction of the ROC is referred to as the "Free Area of the Republic of China" in the Constitution. In most ordinary legislation, the term "Taiwan Area" is used in place of the "Free Area", while Mainland China is referred to as the "Mainland Area". According to the Act Governing Relations Between Peoples of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area, originally promulgated in 1992 and last amended in 2004, the "Taiwan Area" refers to "Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu, and any other area under the effective control of the Government" and the "Mainland Area" refers to "the territory of the Republic of China outside the Taiwan Area."
| Name | Old Name (Postal) | Chinese (T) | Pinyin | Abbreviation | Capital | Capital in Chinese |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provinces (省 Shěng) | ||||||
| Andong | Antung | 安東 | Āndōng | 安 ān | Tunghwa (Tonghua) | 通化 |
| Anhui | Anhwei | 安徽 | Ānhuī | 皖 wǎn | Hofei (Hefei) | 合肥 |
| Chahar | Chahar | 察哈爾 | Cháhā'ěr | 察 chá | Changyuan (Zhangjiakou) | 張垣(張家口) |
| Fujian | Fukien | 福建 | Fújiàn | 閩 mǐn | Foochow (Fuzhou) | 福州 |
| Gansu | Kansu | 甘肅 | Gānsù | 甘 gān or 隴 lǒng | Lanchow (Lanzhou) | 蘭州 |
| Guangdong | Kwangtung | 廣東 | Guǎngdōng | 粵 yuè | Canton (Guangzhou) | 廣州 |
| Guangxi | Kwangsi | 廣西 | Guǎngxī | 桂 guì | Kweilin (Guilin) | 桂林 |
| Guizhou | Kweichow | 貴州 | Guìzhōu | 黔 qian or 貴 gui | Kweiyang (Guiyang) | 貴陽 |
| Hebei | Hopeh | 河北 | Háběi | 冀 jì | Tsingyuan (Baoding) | 清苑(保定) |
| Heilongjiang | Heilungkiang | 黑龍江 | Hēilóngjiāng | 黑 hēi | Peian (Bei'an) | 北安 |
| Hejiang | Hokiang | 合江 | Héjiāng | 合 hé | Chiamussu (Jiamusi) | 佳木斯 |
| Henan | Honan | 河南 | Hénán | 豫 yù | Kaifeng (Kaifeng) | 開封 |
| Hubei | Hupeh | 湖北 | Húběi | 鄂 è | Wuchang (Wuchang) | 武昌 |
| Hunan | Hunan | 湖南 | Húnán | 湘 xiāng | Changsha (Changsha) | 長沙 |
| Jiangsu | Kiangsu | 江蘇 | Jiāngsū | 蘇 sū | Chinkiang (Zhenjiang) | 鎮江 |
| Jiangxi | Kiangsi | 江西 | Jiāngxī | 贛 gàn | Nanchang (Nanchang) | 南昌 |
| Jilin | Kirin | 吉林 | Jílín | 吉 jí | Kirin (Jilin) | 吉林 |
| Liaobei | Liaopeh | 遼北 | Liáoběi | 洮 táo | Liaoyuan (Liaoyuan) | 遼源 |
| Liaoning | Liaoling | 遼寧 | Liáoníng | 遼 liáo | Shenyang (Shenyang) | 瀋陽 |
| Ningxia | Ningsia | 寧夏 | Níngxià | 寧 níng | Yinchuan (Yinchuan) | 銀川 |
| Nenjiang | Nunkiang | 嫩江 | Nènjiāng | 嫩 nèn | Tsitsihar (Qiqihar) | 齊齊哈爾 |
| Qinghai | Tsinghai | 青海 | Qīnghǎi | 青 qīng | Sining (Xining) | 西寧 |
| Rehe | Rehe(Jehol) | 熱河 | Rèhé | 熱 rè | Chengteh (Chengde) | 承德 |
| Shaanxi | Shensi | 陝西 | Shǎnxī | 陝 shǎn or 秦 qín | Sian (Xi'an) | 西安 |
| Shandong | Shantung | 山東 | Shāndōng | 魯 lǔ | Tsinan (Jinan) | 濟南 |
| Shanxi | Shansi | 山西 | Shānxī | 晉 jin | Taiyuan (Taiyuan) | 太原 |
| Sichuan | Szechwan | 四川 | Sìchuān | 川 chuān or 蜀 shǔ | Chengtu (Chengdu) | 成都 |
| Songjiang | Sungkiang | 松江 | Sōngjiāng | 松 sōng | Mutankiang (Mudanjiang) | 牡丹江 |
| Suiyuan | Suiyuan | 綏遠 | Suīyuǎn | 綏 suī | Kweisui (Hohhot) | 歸綏(呼和浩特) |
| Taiwan | Taiwan | 臺灣 | Táiwān | 臺 tái | Zhongxing Village1 | 中興新村 |
| Xikang | Sikang | 西康 | Xīkāng | 康 kāng | Kangting (Kangding) | 康定 |
| Xing'an | Hsingan | 興安 | Xīng'ān | 興 xīng | Hailar (Hulunbuir) | 海拉爾(呼倫貝爾) |
| Xinjiang | Sinkiang | 新疆 | Xīnjiāng | 新 xīn or 疆 jiāng | Tihwa (Urumqi) | 迪化(烏魯木齊) |
| Yunnan | Yunnan | 雲南 | Yúnnán | 滇 diān or 雲 yún | Kunming (Kunming) | 昆明 |
| Zhejiang | Chekiang | 浙江 | Zhèjiāng | 浙 zhè | Hangchow (Hangzhou) | 杭州 |
| Special administrative region (特別行政區 Tèbié Xíngzhèngqǖ) | ||||||
| Hainan | Hainan | 海南 | Hǎinan | 瓊 qióng | Haikow (Haikou) | 海口 |
| Regions (地方 Dìfāng) | ||||||
| Outer Mongolia | Mongolia Area | 蒙古 | Ménggǔ | 蒙 méng | Kulun (Ulaanbaatar) | 庫倫(烏蘭巴托) |
| Tibet | Tibet Area | 西藏 | Xīzàng | 藏 zàng | Lhasa | 拉薩 |
| Municipalities (直轄市 Zhíxiáshì) | ||||||
| Beiping (Beijing) | Peiping (Peking) | 北平 | Běipíng | 平 píng | (Dongcheng District) | 東城區 |
| Chongqing | Chungking | 重慶 | Chóngqìng | 渝 yú | (Yuzhong District) | 渝中區 |
| Dalian | Dairen | 大連 | Dàlián | 連 lián | (Xigang District) | 西崗區 |
| Guangzhou | Kwangchow (Canton) | 廣州 | Guǎngzhōu | 穗 suì | (Yuexiu District) | 越秀區 |
| Hankou (Wuhan) | Hankow | 漢口 | Hànkǒu | 漢 hàn | (Jiang'an District) | 江岸區 |
| Harbin | Harbin | 哈爾濱 | Hā'ěrbīn | 哈 hā | (Nangang District) | 南崗區 |
| Kaohsiung2 | Takao, Takow | 高雄 | Gāoxióng | 高 gāo | (Lingya District) | 苓雅區 |
| Nanjing | Nanking | 南京 | Nánjīng | 京 jīng | (Xuanwu District) | 玄武區 |
| Qingdao | Tsingtao | 青島 | Qīngdǎo | 青 qīng | (Shinan District) | 市南區 |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | 上海 | Shànghǎi | 滬 hù | (Huangpu District) | 黄浦區 |
| Shenyang | Shenyang | 瀋陽 | Shěnyáng | 瀋 shěn | (Shenhe District) | 瀋河區 |
| Taipei2 | Taipeh, Taihoku | 臺北 | Táiběi | 北 běi | (Xinyi District) | 信義區 |
| Taichung3 | Taichū | 臺中 | Táizhōng | 中 zhōng | To Be Determined | To Be Determined |
| Tainan3 | Tainan | 臺南 | Táinán | 南 nán | To Be Determined | To Be Determined |
| Tianjin | Tientsin | 天津 | Tiānjīn | 津 jīn | (Heping District) | 和平區 |
| Xi'an | Sian | 西安 | Xī'ān | 鎬 hào | (Weiyang District) | 未央區 |
| Xinbei3 | 新北 | Xīnběi | 新 xīn | To Be Determined | To Be Determined | |
- The capital of Taiwan Province was moved to Zhongxing Village from Taipei in the 1960s.
- Taipei, Kaohsiung were elevated in 1967 and 1979, respectively, after the ROC government had moved to Taipei in 1949.
- Taichung, Tainan, and Xinbei will be elevated on 25 December 2010 since last reform.
References
- ↑ Taiwan Review-Gone with the Times
- ↑ "國立教育廣播電台新聞 (2007-10-01): 歷時28年 臺北縣今升格為準直轄市 (After 28 years, Taipei County today is promoted to quasi-municipality status)". http://www.webcitation.org/5hjOGAvUG.
- ↑ "Liberty Times (2008-12-27): 三都十五縣 馬指示漸進推動 (Ma directs gradual progression towards 3 municipalities and 15 counties)". http://www.webcitation.org/5hjOy5NgD.
- ↑ "Liberty Times (2009-06-24): 縣市升格 北中高過關 南縣市補考 (Promotion of Cities and Counties: Taipei, Taichung, and Kaohsiung approved; Tainan awaits further examination)". http://www.webcitation.org/5hmHkK2Ql.
- ↑ Wikinews (2009-06-29): 臺灣再添直轄市; http://www.nownews.com/2009/06/29/11468-2471373.htm
- ↑ Taipei Times (2009-06-25): City upgrades draw mixed reaction
- ↑ "Hanyu Pinyin to be standard system in 2009". Taipei Times. 2008-09-18. http://www.taipeitimes.com/News/taiwan/archives/2008/09/18/2003423528.
- ↑ "Gov't to improve English-friendly environment". The China Post. 2008-09-18. http://www.chinapost.com.tw/taiwan/national/national%20news/2008/09/18/175155/Gov%27t-to.htm.
- ↑ National Institute for Compilation and Translation of the Republic of China (Taiwan): Geograpy Textbook for Junior High School Volume 1 (1993 version): Lesson 10: pages 47 to 49
See also
- History of the Republic of China
- Political divisions of China
- Political divisions of Taiwan (1895-1945)
- Lists of Taiwanese counties and cities: by area · by population · by population density
- ISO 3166-2:TW
External links
- 內政部地政司 (Department of Land Administration, Ministry of the Interior): Romanizations for county-level and township-level entities
- Map of ROC (including Quemoy and Matsu)
- Fuchien Provincial Government
- Taiwan Provincial Government
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||